type: doc layout: reference category: "Collections"
title: "集合概述"
Kotlin 集合概述
Kotlin 标准库提供了一整套用于管理集合的工具,集合是可变数量(可能为零)的一组条目,各种集合对于解决问题都具有重要意义,并且经常用到。
集合是大多数编程语言的常见概念,因此如果熟悉像 Java 或者 Python 语言的集合,那么可以跳过这一介绍转到详细部分。
集合通常包含相同类型的一些(数目也可以为零)对象。集合中的对象称为元素或条目。例如,一个系的所有学生组成一个集合,可以用于计算他们的平均年龄。 以下是 Kotlin 相关的集合类型:
- List 是一个有序集合,可通过索引(反映元素位置的整数)访问元素。元素可以在 list 中出现多次。列表的一个示例是一句话:有一组字、这些字的顺序很重要并且字可以重复。
- Set 是唯一元素的集合。它反映了集合(set)的数学抽象:一组无重复的对象。一般来说 set 中元素的顺序并不重要。例如,字母表是字母的集合(set)。
- Map(或者字典)是一组键值对。键是唯一的,每个键都刚好映射到一个值。值可以重复。map 对于存储对象之间的逻辑连接非常有用,例如,员工的 ID 与员工的位置。
Kotlin 让你可以独立于所存储对象的确切类型来操作集合。换句话说,将 String 添加到 String list 中的方式与添加 Int 或者用户自定义类的到相应 list 中的方式相同。
因此,Kotlin 标准库为创建、填充、管理任何类型的集合提供了泛型的(通用的,双关)接口、类与函数。
这些集合接口与相关函数位于 kotlin.collections 包中。我们来大致了解下其内容。
集合类型
Kotlin 标准库提供了基本集合类型的实现: set、list 以及 map。 一对接口代表每种集合类型:
- 一个 只读 接口,提供访问集合元素的操作。
- 一个 可变 接口,通过写操作扩展相应的只读接口:添加、删除和更新其元素。
请注意,更改可变集合不需要它是以 var 定义的变量:写操作修改同一个可变集合对象,因此引用不会改变。
但是,如果尝试对 val 集合重新赋值,你将收到编译错误。
fun main() {
//sampleStart
val numbers = mutableListOf("one", "two", "three", "four")
numbers.add("five") // 这是可以的
//numbers = mutableListOf("six", "seven") // 编译错误
//sampleEnd
}
只读集合类型是型变的。
这意味着,如果类 Rectangle 继承自 Shape,则可以在需要 List <Shape> 的任何地方使用 List <Rectangle>。
换句话说,集合类型与元素类型具有相同的子类型关系。 map 在值(value)类型上是型变的,但在键(key)类型上不是。
反之,可变集合不是型变的;否则将导致运行时故障。 如果 MutableList <Rectangle> 是 MutableList <Shape> 的子类型,你可以在其中插入其他 Shape 的继承者(例如,Circle),从而违反了它的 Rectangle 类型参数。
下面是 Kotlin 集合接口的图表:
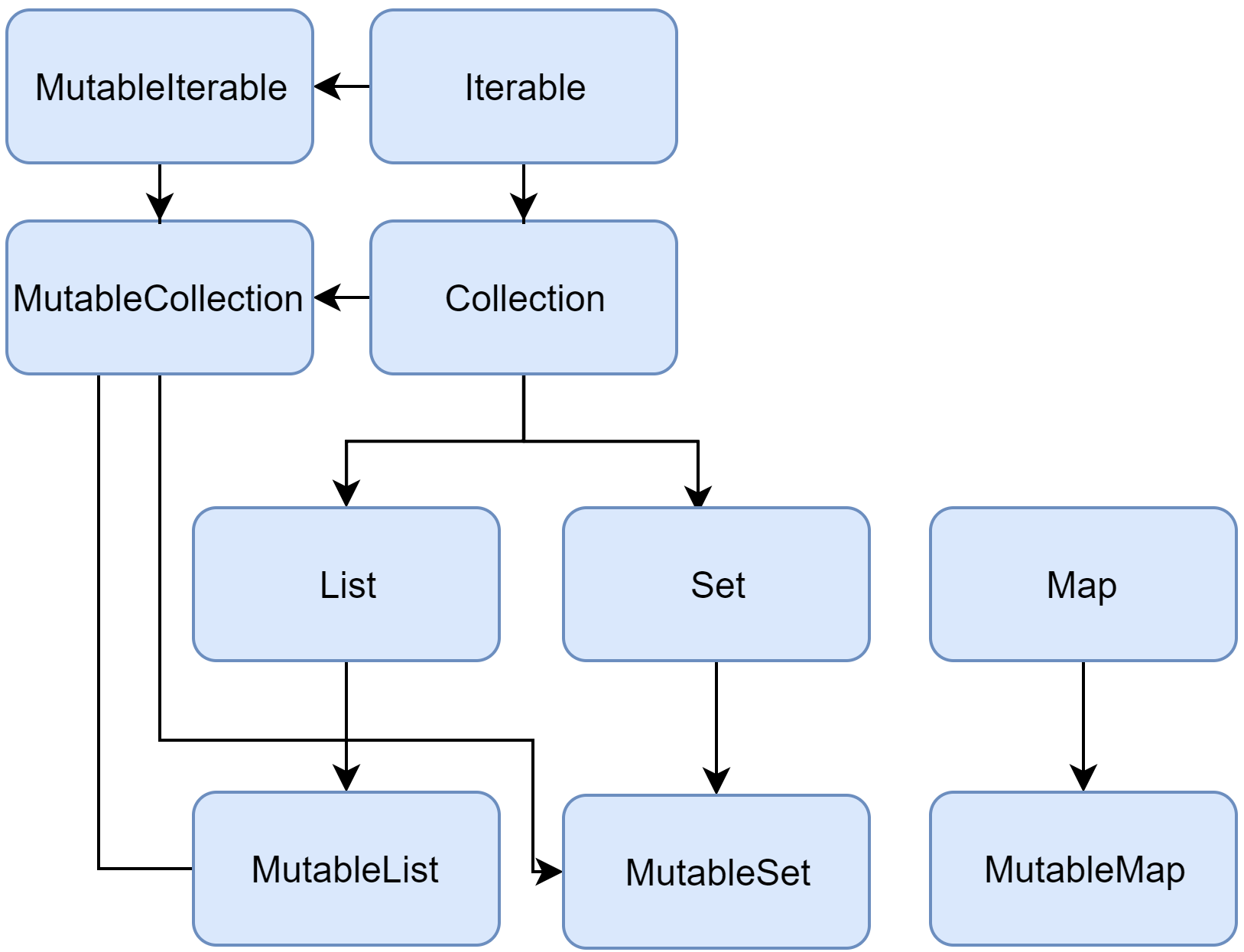
让我们来看看接口及其实现。
Collection
Collection<T> 是集合层次结构的根。此接口表示一个只读集合的共同行为:检索大小、检测是否为成员等等。
Collection 继承自 Iterable <T> 接口,它定义了迭代元素的操作。可以使用 Collection 作为适用于不同集合类型的函数的参数。对于更具体的情况,请使用 Collection 的继承者: List 与 Set。
fun printAll(strings: Collection<String>) {
for(s in strings) print("$s ")
println()
}
fun main() {
val stringList = listOf("one", "two", "one")
printAll(stringList)
val stringSet = setOf("one", "two", "three")
printAll(stringSet)
}
MutableCollection 是一个具有写操作的 Collection 接口,例如 add 以及 remove。
fun List<String>.getShortWordsTo(shortWords: MutableList<String>, maxLength: Int) {
this.filterTo(shortWords) { it.length <= maxLength }
// throwing away the articles
val articles = setOf("a", "A", "an", "An", "the", "The")
shortWords -= articles
}
fun main() {
val words = "A long time ago in a galaxy far far away".split(" ")
val shortWords = mutableListOf<String>()
words.getShortWordsTo(shortWords, 3)
println(shortWords)
}
List
List<T> 以指定的顺序存储元素,并提供使用索引访问元素的方法。索引从 0 开始 – 第一个元素的索引 – 直到 最后一个元素的索引 即 (list.size - 1)。
fun main() {
//sampleStart
val numbers = listOf("one", "two", "three", "four")
println("Number of elements: ${numbers.size}")
println("Third element: ${numbers.get(2)}")
println("Fourth element: ${numbers[3]}")
println("Index of element \"two\" ${numbers.indexOf("two")}")
//sampleEnd
}
List 元素(包括空值)可以重复:List 可以包含任意数量的相同对象或单个对象的出现。 如果两个 List 在相同的位置具有相同大小和相同结构的元素,则认为它们是相等的。
data class Person(var name: String, var age: Int)
fun main() {
//sampleStart
val bob = Person("Bob", 31)
val people = listOf<Person>(Person("Adam", 20), bob, bob)
val people2 = listOf<Person>(Person("Adam", 20), Person("Bob", 31), bob)
println(people == people2)
bob.age = 32
println(people == people2)
//sampleEnd
}
MutableList 是可以进行写操作的 List,例如用于在特定位置添加或删除元素。
fun main() {
//sampleStart
val numbers = mutableListOf(1, 2, 3, 4)
numbers.add(5)
numbers.removeAt(1)
numbers[0] = 0
numbers.shuffle()
println(numbers)
//sampleEnd
}
如你所见,在某些方面,List 与数组(Array)非常相似。 但是,有一个重要的区别:数组的大小是在初始化时定义的,永远不会改变; 反之,List 没有预定义的大小;作为写操作的结果,可以更改 List 的大小:添加,更新或删除元素。
在 Kotlin 中,List 的默认实现是 ArrayList,可以将其视为可调整大小的数组。
Set
Set<T> 存储唯一的元素;它们的顺序通常是未定义的。null 元素也是唯一的:一个 Set 只能包含一个 null。当两个 set 具有相同的大小并且对于一个 set 中的每个元素都能在另一个 set 中存在相同元素,则两个 set 相等。
fun main() {
//sampleStart
val numbers = setOf(1, 2, 3, 4)
println("Number of elements: ${numbers.size}")
if (numbers.contains(1)) println("1 is in the set")
val numbersBackwards = setOf(4, 3, 2, 1)
println("The sets are equal: ${numbers == numbersBackwards}")
//sampleEnd
}
MutableSet 是一个带有来自 MutableCollection 的写操作接口的 Set。
Set的默认实现 - LinkedHashSet – 保留元素插入的顺序。
因此,依赖于顺序的函数,例如 first() 或 last(),会在这些 set 上返回可预测的结果。
fun main() {
//sampleStart
val numbers = setOf(1, 2, 3, 4) // LinkedHashSet is the default implementation
val numbersBackwards = setOf(4, 3, 2, 1)
println(numbers.first() == numbersBackwards.first())
println(numbers.first() == numbersBackwards.last())
//sampleEnd
}
另一种实现方式 – HashSet – 不声明元素的顺序,所以在它上面调用这些函数会返回不可预测的结果。但是,HashSet 只需要较少的内存来存储相同数量的元素。
Map
Map<K, V> 不是 Collection 接口的继承者;但是它也是 Kotlin 的一种集合类型。
Map 存储 键-值 对(或 条目);键是唯一的,但是不同的键可以与相同的值配对。Map 接口提供特定的函数进行通过键访问值、搜索键和值等操作。
fun main() {
//sampleStart
val numbersMap = mapOf("key1" to 1, "key2" to 2, "key3" to 3, "key4" to 1)
println("All keys: ${numbersMap.keys}")
println("All values: ${numbersMap.values}")
if ("key2" in numbersMap) println("Value by key \"key2\": ${numbersMap["key2"]}")
if (1 in numbersMap.values) println("The value 1 is in the map")
if (numbersMap.containsValue(1)) println("The value 1 is in the map") // 同上
//sampleEnd
}
无论键值对的顺序如何,包含相同键值对的两个 Map 是相等的。
fun main() {
//sampleStart
val numbersMap = mapOf("key1" to 1, "key2" to 2, "key3" to 3, "key4" to 1)
val anotherMap = mapOf("key2" to 2, "key1" to 1, "key4" to 1, "key3" to 3)
println("The maps are equal: ${numbersMap == anotherMap}")
//sampleEnd
}
MutableMap 是一个具有写操作的 Map 接口,可以使用该接口添加一个新的键值对或更新给定键的值。
fun main() {
//sampleStart
val numbersMap = mutableMapOf("one" to 1, "two" to 2)
numbersMap.put("three", 3)
numbersMap["one"] = 11
println(numbersMap)
//sampleEnd
}
Map 的默认实现 – LinkedHashMap – 迭代 Map 时保留元素插入的顺序。
反之,另一种实现 – HashMap – 不声明元素的顺序。